In the previous post, I detailed a manual approach to installing both the codedeploy and cloudwatch agent. SSM State Manager is a service provided by SSM that keeps the nodes you define in a predefined state. A State Manager Association is a configuration that state manager uses to maintain the state of the instances. An example could be to ensure the instance has certain software installed and running after it’s created.
Using the terraform resource aws_ssm_association, we can leverage the State Manager to install and configure both the codedeploy and cloudwatch agents after the instance is initialized. The state manager association will run the given document name with the parameters to install the software.
To install CodeDeploy and Cloudwatch agents, we use the AWS-ConfigureAWSPackage document and pass in the parameters of Install and the name of the software. Note that the unlike the UI, the aws_ssm_association only allows you to define the run command output logs to an S3 bucket. Example below is the TF definition for installing CodeDeploy agent:
resource "aws_ssm_association" "install-codedeploy-agent" {
name = "AWS-ConfigureAWSPackage"
targets {
key = "tag:Name"
values = ["CodeDeployDemo"]
}
output_location {
s3_bucket_name = "tf-ssm-association"
s3_key_prefix = "codedeploy-agent"
s3_region = "eu-west-2"
}
parameters = {
action = "Install"
name = "AWSCodeDeployAgent"
}
wait_for_success_timeout_seconds = 30
}The use of wait_for_success_timeout_seconds is important in keeping the sequence of the associations in sync. Since we need to install the CodeDeploy agent first, we will wait for a timeout of 30 seconds before invoking the second association to install the Cloudwatch agent. An example TF definition for installing the Cloudwatch Agent is as follows:
resource "aws_ssm_association" "install-cloudwatch-agent" {
name = "AWS-ConfigureAWSPackage"
targets {
key = "tag:Name"
values = ["CodeDeployDemo"]
}
parameters = {
action = "Install"
name = "AmazonCloudWatchAgent"
}
output_location {
s3_bucket_name = "tf-ssm-association"
s3_key_prefix = "cloudwatch-agent"
s3_region = "eu-west-2"
}
depends_on = [aws_ssm_association.install-codedeploy-agent]
wait_for_success_timeout_seconds = 30
}Note the use of depends_on and wait_for_success_timeout_seconds. TF will wait till the previous commands are completed before it creates the second association.
To configure the Cloudwatch agent to send the CodeDeploy logs to Cloudwatch, we run a third association to read a configuration file stored in SSM. This third association will wait until the Cloudwatch Agent is installed before running:
resource "aws_ssm_association" "configure-cloudwatch-agent" {
name = "AmazonCloudWatch-ManageAgent"
targets {
key = "tag:Name"
values = ["CodeDeployDemo"]
}
parameters = {
action = "configure"
mode = "ec2"
optionalConfigurationSource = "ssm"
optionalConfigurationLocation = "testagentcfg"
optionalRestart = "yes"
}
output_location {
s3_bucket_name = "tf-ssm-association"
s3_key_prefix = "cloudwatch-agent-configure"
s3_region = "eu-west-2"
}
depends_on = [
aws_ssm_association.install-cloudwatch-agent
]
wait_for_success_timeout_seconds = 30
}The final state association waits for the cloudwatch agent to be running within a timeout range of 30 seconds. It applies the cloudwatch agent config file testagentcfg which is stored as an SSM parameter and calls the document AmazonCloudWatch-ManageAgent to apply the configuration.
By using this tiered approach, I was able to automate the process of setting up the EC2 instance with the required software after initialization.
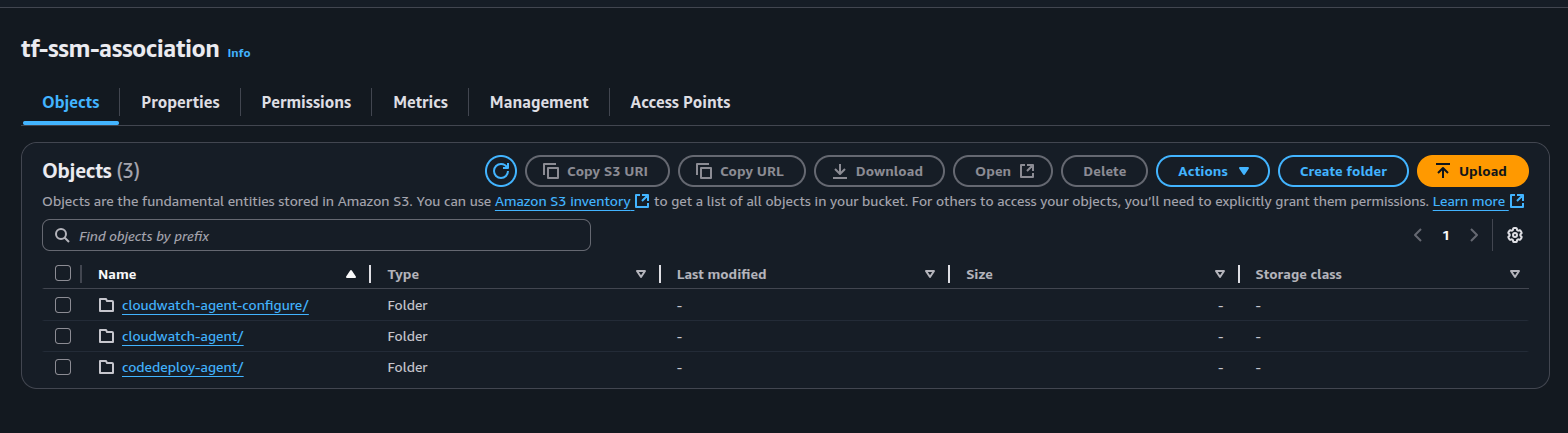
The log files are stored in the provided S3 bucket and one could utilize a service such as Athena to parse the log files.
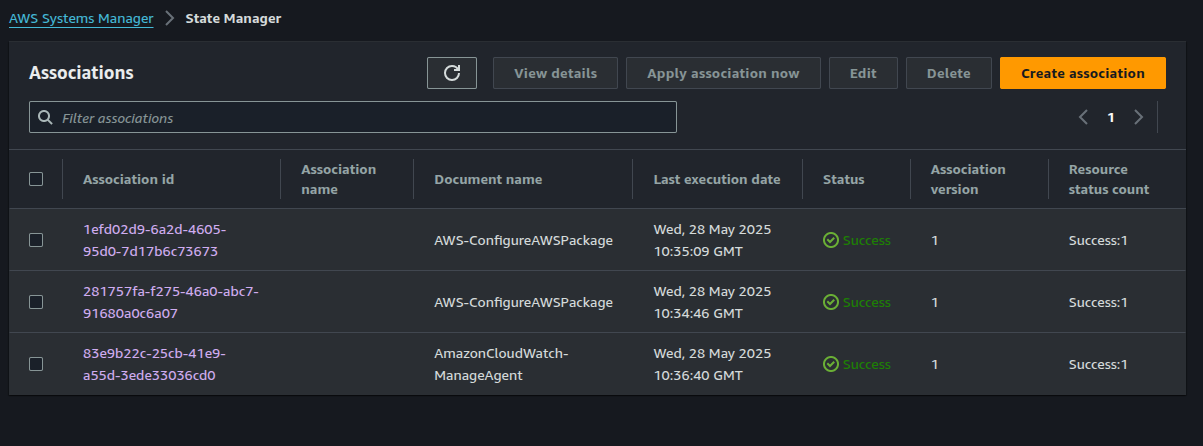
The screenshot belows show the state association created:
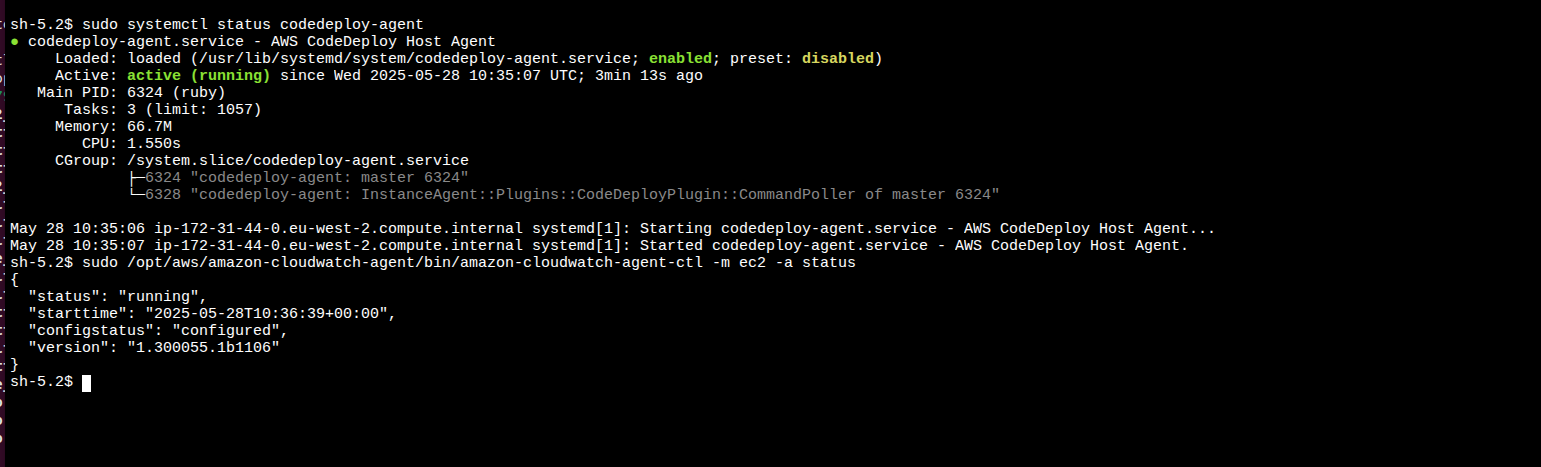
The screenshots below show both the agents setup and running on the target instance:
The screenshot below shows the state association logs output to target s3 bucket: