In a previous post, I discussed how to apply TargetTracking scaling to an ECS service. Another scaling policy is Step Scaling, which scales application capacity when a cloudwatch alarm is breached. The application autoscaling service will increase / decrease the capacity based on the upper and lower interval values specified in the step scaling policy adjustments.
Step Scaling scales capacity using a set of adjustments known as step adjustments. The size of the adjustment depends on the magnitude of the alarm breach. For example, if the breach exceeds the first threshold, the first step adjustment is applied. If the breach exceeds the second threshold, the second step adjustment will be applied. This allows for more granular scaling which supports changes in ranges of the metric rather than a static value.
The main differences with Target Tracking scaling is:
-
We are monitoring metrics based on a range set by lower and upper bound values in relation to a target threshold.
-
We require a cloudwatch alarm for each step scaling policy as the step scaling policy can only be activated when the alarm is in breach.
For this example, we are creating an alarm that sets the target memory threshold to be at 10%. If the memory usage exceeds the threshold, the step scaling policy defined in alarm_actions will be activated.
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "ecs_service_memory_scale_out_alarm" {
alarm_name = "Memory utilization greater than 10%"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanThreshold"
evaluation_periods = "1"
metric_name = "MemoryUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/ECS"
period = "60"
statistic = "Average"
threshold = "10"
alarm_description = "Alarm if Memory Utilization is greater than 10%"
dimensions = {
ClusterName = aws_ecs_cluster.flaskapp.name
ServiceName = aws_ecs_service.flaskapp.name
}
alarm_actions = [aws_appautoscaling_policy.ecs_memory_scale_up_policy.arn]
}A full list of available metric names for ECS can be found in AWS ECS Cloudwatch Metrics documentation.
Note that we set the threshold of the alarm to be 10 with a greater than comparison operator, which means any usage above 10% will trigger the step scaling policy as defined under alarm_actions. The namespace is set to AWS/ECS and the dimensions are set to the cluster and service name, which are recommended in AWS ECS Cloudwatch Metrics.
The step scaling policy triggered the alarm is defined below:
resource "aws_appautoscaling_policy" "ecs_memory_scale_up_policy" {
name = "memory-scale-up"
policy_type = "StepScaling"
resource_id = aws_appautoscaling_target.ecs_target.resource_id
scalable_dimension = aws_appautoscaling_target.ecs_target.scalable_dimension
service_namespace = aws_appautoscaling_target.ecs_target.service_namespace
step_scaling_policy_configuration {
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
metric_aggregation_type = "Average"
cooldown = 60
step_adjustment {
metric_interval_lower_bound = 0
metric_interval_upper_bound = 10
scaling_adjustment = 1
}
step_adjustment {
metric_interval_lower_bound = 10
metric_interval_upper_bound = 25
scaling_adjustment = 2
}
step_adjustment {
metric_interval_lower_bound = 25
scaling_adjustment = 3
}
}
}This policy is linked to the ECS service as a target. It defines three step adjustments which define the intervals or ranges of the alarm breach and the corresponding adjustments to make. This example configuration creates the following scaling policies with the alarm threshold:
-
Lower bound: 0, upper bound: 10. If memory usage is > 10 and memory usage < 20, increase the capacity by 1. ( alarm threshold + lowerbound, alarm threshold + upper bound )
-
Lower bound: 10, upper bound: 25. If 20 < memory usage < 35, increase the capacity by 2. ( alarm threshold + lower bound , alarm threshold + upper bound )
-
If memory usage > 35, increase the capacity by 3. ( alarm threshold + lower bound )
To define the scale in action, we define a separate alarm that scales in the service when the threshold is less than a target value:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "ecs_service_memory_scale_in_alarm" {
alarm_name = "Memory utilization less than 10%"
comparison_operator = "LessThanOrEqualToThreshold"
evaluation_periods = "1"
metric_name = "MemoryUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/ECS"
period = "60"
statistic = "Average"
threshold = "10"
alarm_description = "Alarm if Memory Utilization is less than 10%"
dimensions = {
ClusterName = aws_ecs_cluster.flaskapp.name
ServiceName = aws_ecs_service.flaskapp.name
}
alarm_actions = [aws_appautoscaling_policy.ecs_memory_scale_in_policy.arn]
}The alarm defines a threshold value of 10 with a less than or equal to threshold comparison, which means if the memory usage falls below 10%, it will trigger the scale in policy, which is defined below:
resource "aws_appautoscaling_policy" "ecs_memory_scale_in_policy" {
name = "memory-scale-in"
policy_type = "StepScaling"
resource_id = aws_appautoscaling_target.ecs_target.resource_id
scalable_dimension = aws_appautoscaling_target.ecs_target.scalable_dimension
service_namespace = aws_appautoscaling_target.ecs_target.service_namespace
step_scaling_policy_configuration {
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
metric_aggregation_type = "Average"
cooldown = 60
step_adjustment {
metric_interval_upper_bound = 0
scaling_adjustment = -1
}
}
}The scale in policy defines a single step adjustment which has an upper bound value of 0. This creates the following scaling policy:
- Upper bound: 0. If memory < 10, decrease capacity by 1. ( alarm threshold + upper bound )
If the memory usage falls below 10%, we decrease the capacity by 1 task unit.
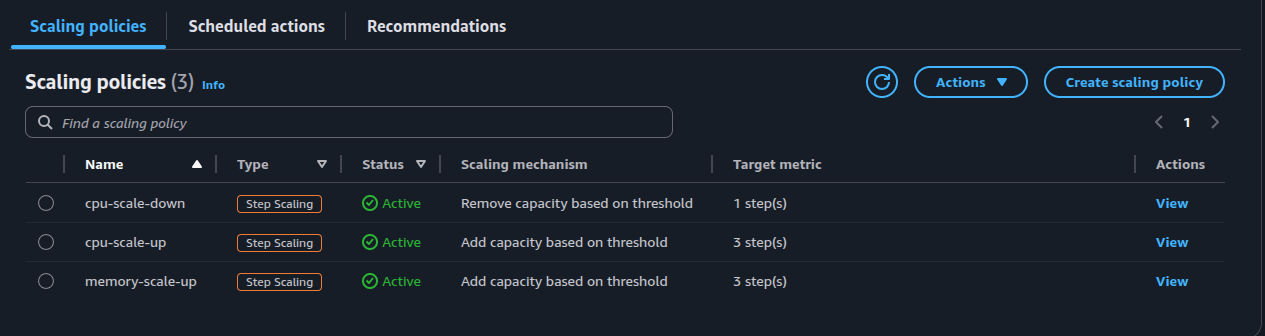
The screenshot below shows the step scaling policies defined in ECS:

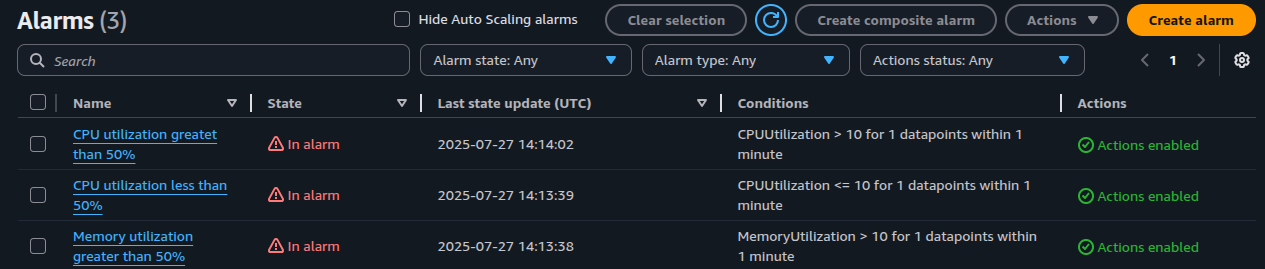
Since we have deliberately defined low threshold values for testing purposes, the cloudwatch alarms start to report a breach shortly after the application is deployed.
The alarms trigger the step scaling policies, which started to provision additional task units:
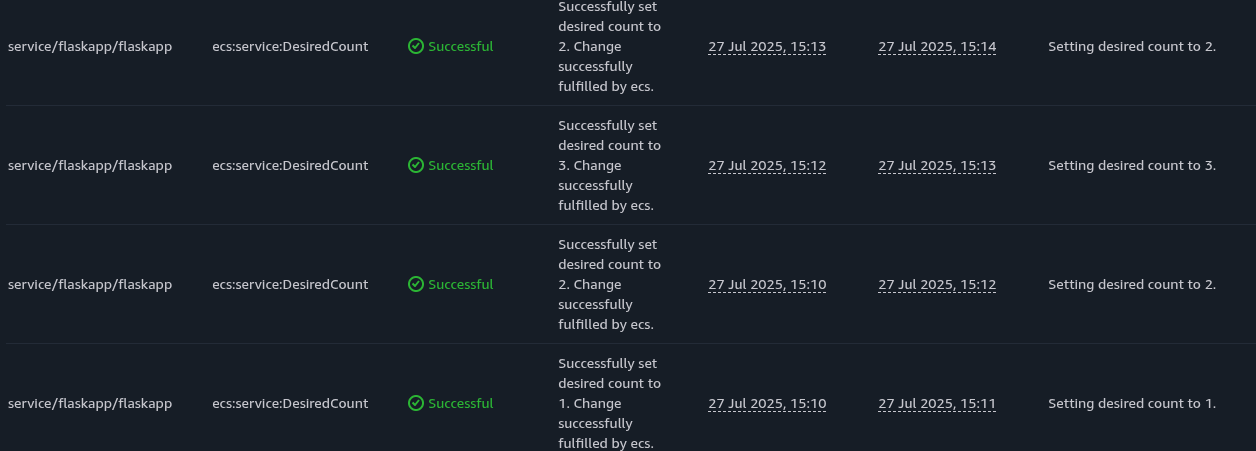
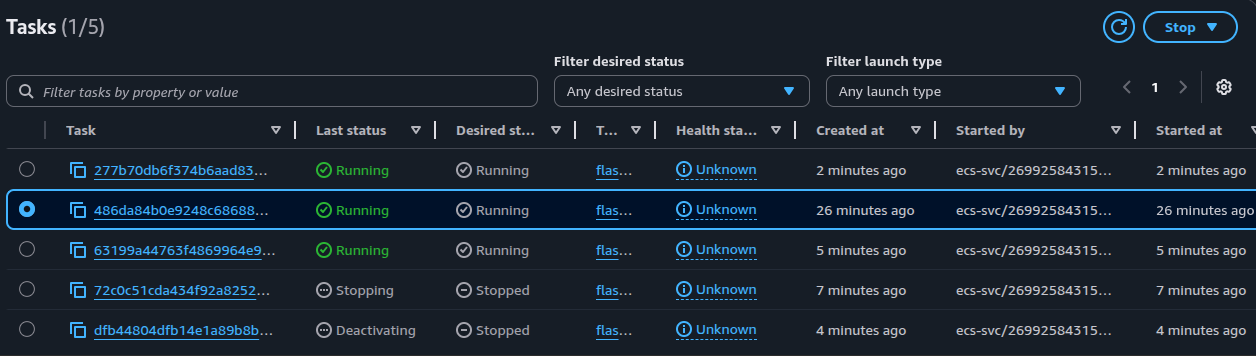
Note that under the service autoscaling logs screen, we see the desired count of the services increased to 3 and then scaled in to 2 units. This is due to the CPU scale in alarm activating shortly after the memory scale out alarms have activated. In real production usage, there needs to be careful planning on the scaling processes and the metrics threshold to set to prevent an aggressive loop of scale in and scale out events.