In a recent python Flask project, I started to create a CI/CD pipeline to manage the application development process. One of the requirements was to run unit tests for every single pull request made. While I am not averse to using mocks and stubs and the general consensus is that we should not be using an external dependency such as a database for running unit tests, my opinion is that we shouldn’t mock the core database models and services as using mocks and stubs can be brittle and lead to hard to debug test failures.
Github actions support running Jobs service containers wiithin a job definition in a workflow. It runs the specified container on the runner host and can be accessed via localhost through the mapped port.
The example Github workflow below specifies the service block for running an external Postgresql container in a job:
env:
RDS_HOSTNAME: localhost
RDS_PORT: "5432"
RDS_USERNAME: flaskapp_test
RDS_DB_NAME: flaskapp_test
RDS_PASSWORD: $
jobs:
unit-tests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
services:
postgres:
image: postgres
env:
POSTGRES_USER: $
POSTGRES_DB: $
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: $
options: >-
--health-cmd pg_isready
--health-interval 10s
--health-timeout 5s
--health-retries 5
ports:
# Maps tcp port 5432 on service container to the host
- 5432:5432We specify the postgres image as the source image and pass in the required credentials via the Github environment variables. We map the database port of 5432 to the runner host port. We also set the rds hostname to be localhost which is used by the SQLAlchemy configuration in the application.
Next, we define the steps to run the unit-tests:
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: "3.12.11"
cache: "pip"
- name: Install dependenciess
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- name: Unit Tests
run: |
mkdir -p logs
touch logs/microblog.log
nohup python -u -m aiosmtpd -n -c aiosmtpd.handlers.Debugging -l 0.0.0.0:8030 &
python -m flask db upgrade
python -m pytest --ignore=tests/integration -p no:cacheprovider --junitxml=junit/test-results.xml --cov-report=html --cov-report=term --cov=board
- name: Test Report
uses: phoenix-actions/test-reporting@v15
if: success() || failure()
with:
name: Unit test summary
path: junit/*.xml
reporter: java-junit
output-to: step-summary
- name: Upload pytest tests results
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: test-results
path: |
junit/
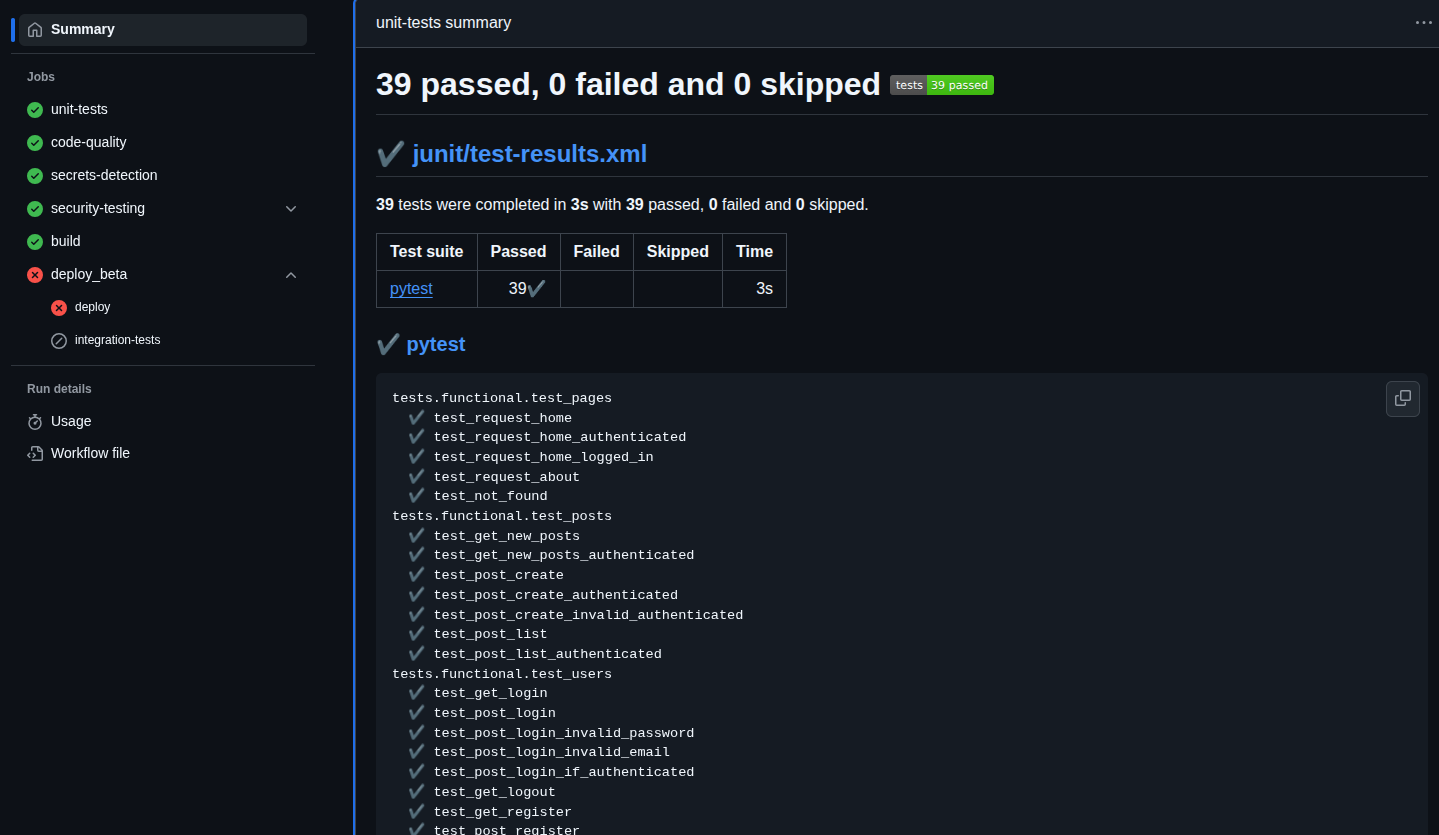
htmlcov/The steps setup the dependencies and configurations required to run the unit tests using pytest. It sets up the test database by running flask db upgrade which runs the migrations and sets up the database schema using SQLAlchemy.
It ignores the intergation test suite and outputs the test results using JUnit format and test coverage reports in html. The JUnit XML files are parsed and output as a step summary, visible in the workflow summary page. The test results are packaged and uploaded as artifacts. The screenshot below shows a successful run of the test suite: